What Is the Normal Respiratory Rate of a Child?
The normal respiration rate can range slightly from person to person, generally doctors and respiratory therapists consider normal.
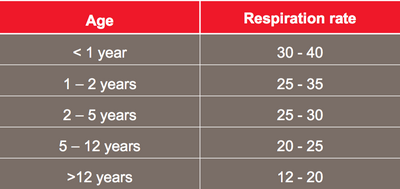
The normal respiration rate for normal adults is anywhere from twelve to twenty breaths per minute. In this respiration rate, the oxygen enters the lungs at a similar rate to the body creates it, at a steady rate. If the breathing stops suddenly, the breathing will slow down, the gas will be expelled from the lungs and the heart rate will slow down, usually causing shortness of breath.
The normal respiration rate for children is also very close to that of adults, most times with very little variation in the different respiratory system functions that happen as a result. Many times the respiratory system becomes slower in children due to problems that may occur in the tonsils or the adenoids.
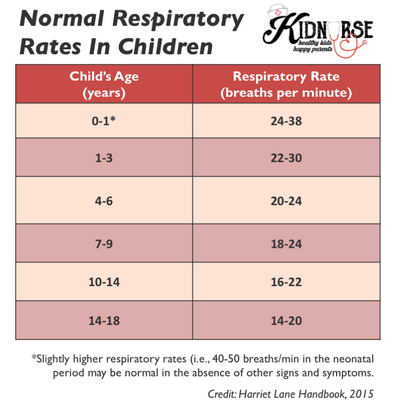
Often, when a child has a cold they can’t breathe. Children with colds often have shortness of breath that is very noticeable.
A child’s respiratory system is quite complex and it can be extremely difficult to diagnose. One of the main symptoms of respiratory illness in children is wheezing. Wheezing in children is usually found as the child coughs and inhales through the mouth.
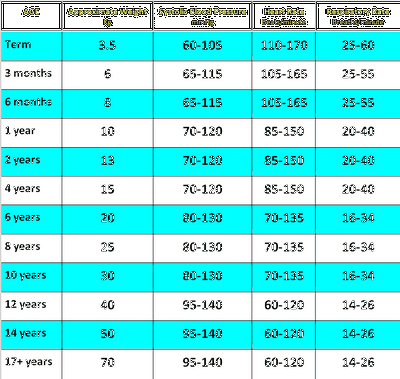
A cough is a symptom of an upper respiratory infection, therefore wheezing is one of the signs of bronchial pneumonia or some other upper respiratory infection.
This respiratory tract is very small and it is made up of air passageways and lungs. These passages are surrounded by tissue that will push the air into the lungs, while the walls are very soft, allowing the lungs to hold the air. The lungs have many pockets and air sacs to trap the air that the lungs need to move.
The respiratory system is connected to the brain via the olfactory nerve, which is located in the nose. The olfactory nerves send a message to the brain about smell to activate the brain’s response system.
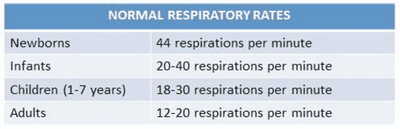
The olfactory nerve is also connected to the central nervous system, so if the child has a problem with smelling, they can still respond to the message the olfactory nerve is sending to the brain.
The normal respiration rate of an adult can range in range between ten to thirty breaths per minute, while children can range between five and fifteen breaths per minute. The number of breaths can be increased or decreased to give the child more or less oxygen than that of an adult. There is no exact age for when a child should be monitored by a respiratory therapist.
If a child is breathing at a normal rate, it is advisable to visit their physician for respiratory monitoring to ensure that they are not having any breathing problems. If breathing stops or there are problems with the breathing, it is time to find out what the cause is and get a diagnosis.
Many times children can use inhalation therapy or use a CPAP machine to open up the airways to allow the patient to breathe normally.
If the respiration rate does not go back to normal after using an inhalation therapy machine, the child may require a bronchodilator. Inhaling pure oxygen is a good method of respiration because it increases the amount of oxygen being able to pass through the lung, but the child cannot breathe through the mouth at first, and the process of breathing will return to normal, thus improving their airway and getting them back into a normal rhythm. If this doesn’t work, then a nebulizer can be used to deliver more oxygen to the lung in a more concentrated form. than what the patient would get from the machine. A pediatrician can tell the patient what medications are used for their respiration and monitor their breathing for signs of asthma or lung disease.