Muscle Relaxers – How Effective Are They?
Muscle relaxers are prescribed for a variety of conditions involving muscle spasms and other signs of muscular tension.
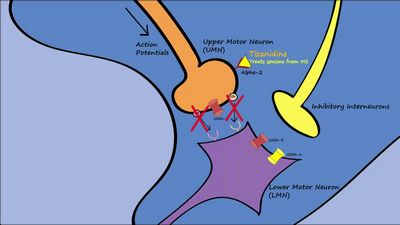
A muscle relaxer is an artificial drug that effects skeletal muscle activity and reduces the muscle strength. It can be used for chronic conditions like muscle spasms, back pain, fibromyalgia, and hyperreflexia to ease symptoms such as pain, muscle spasms, and muscle weakness.
Muscle relaxers affect a variety of muscles in the human body. The term “muscular relaxant” refers to a group of medicines: beta-blockers, alpha-blockers, acetaminophen, muscle relaxers, muscle stimulating agents, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, narcotic analgesics, options, antidepressants, muscle relaxants, and tramadol. The active ingredient in muscle relaxers is muscle relaxor. The medication is given to people with muscle spasms and muscle cramps or after surgery in order to minimize pain or inflammation and help patients with muscle fatigue and aching.
Muscle relaxers can be taken orally, through an injection, or rectally. They are not habit-forming and are only meant for short-term use. They are usually injected into the muscles so that they can penetrate deep into the tissue and affect muscle tissue, not muscle fibers. Muscle relaxers are also given to patients with fibromyalgia or sciatica for pain management. However, it is important to note that muscle relaxers can cause serious side effects, particularly if used in excess.
In order for a muscle relaxer to have the same effect on the muscle as a medication would, it should be taken regularly, the dosage should be increased periodically, and the dose taken at a time that is comfortable and allows the patient to take the maximum possible dose. Patients should avoid taking muscle relaxers in combination with any muscle-strengthening drugs.

Muscle relaxers should also not be used if an underlying illness is present or if you experience a sudden rise in blood pressure or heart rate.
Muscle relaxers can be classified into two groups based on the way they affect muscle cells. Stimulants can be categorized according to how they are absorbed by the target muscle cell. The muscle cells absorb the medication and the drug then travels down the bloodstream to the target muscle, where it is released. In contrast, antagonists can be categorized according to how they bind to receptors on the target cell. They bind the receptor to prevent the receptor from binding to the drug. the drug and then the drug travels down the bloodstream.
Muscle relaxers are most often prescribed for muscle spasms and muscle cramps. They can also be prescribed for fibromyalgia, muscle spasms or back pain, aching joints, neck pain, fibromyalgia, rheumatoid arthritis, fibroid nodules, spondylosis, Lupus, nerve pain, irritable bowel syndrome, or stress ulcers. Muscle relaxers can be taken orally, through an injection, or rectally.
Muscle relaxers can also be used in combination with other medicines in the treatment of diseases such as fibromyalgia, fibroid nodules, or rheumatoid arthritis. However, muscle relaxers should not be taken if the underlying disease is being treated, especially in the case of fibromyalgia. The dose should be carefully measured.
Muscle relaxers are not recommended for people with cardiac problems because of the possibility of damage to the brain and heart due to the side effects of the drug.
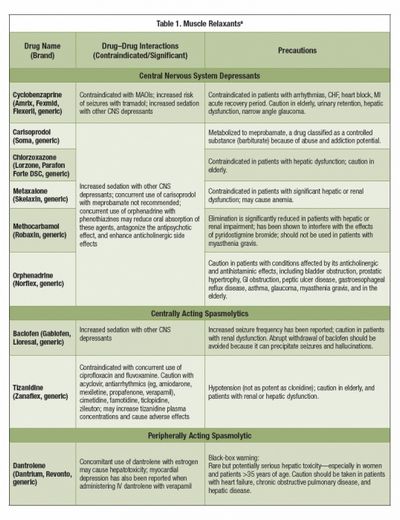
Muscle relaxers should be avoided by those who have a history of allergies. Muscle relaxers should be taken only after consulting your doctor.
Muscle relaxers are widely used in the treatment of mild depression, anxiety, migraine headaches, insomnia, nervousness, and other problems related to anxiety, restlessness, and panic attacks. Muscle relaxers help relieve muscle spasms associated with nervousness and panic attacks by increasing the blood flow in the nervous system. Muscle relaxers can be taken alone, in combination with antidepressants, or in combination with relaxation techniques, including yoga and meditation. Muscle relaxers may also be used for reducing the symptoms of fibromyalgia, spondylosis, fibroids, and Lupus.
Muscle relaxers are available in different forms, depending on the type of molecule they are made of and their strength. A number of medications used for muscle relaxers contain benzodiazepines, antidepressants, alpha-blockers, and beta-blockers. Muscle relaxers are available in various strengths, such as those available in a cream or in a pill. They are available as topical solutions, such as a gel or cream. Some may even be taken in combination with anti-anxiety drugs.
Muscle relaxers are available in various strengths, such as those available in a cream or in a pill. Some may even be taken in combination with relaxation techniques, including yoga and meditation.